
Pulmonary infection caused by Aspergillus glaucus in patient with leucocythemia
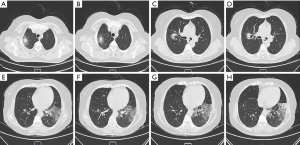
A 52-year-old female was admitted to our hospital with cough, fever and fatigue for a week. Her medical history included leukocytosis and myeloproliferative neoplasma for about 3 months. On physical examination, she appeared shallow breathing with fever up to 38.5 °C and moist rale could be clearly heard on the left lower lobe. Laboratory evaluation at the time of hospital admission revealed as follows: leukocyte count 20.00×109/L, absolute neutrophil count 14.72×109/L, platelet count 400×109/L, procalcitonin 1.22 ng/mL. The galactomannan antibody IgM of aspergillus was 132.19 Au/mL, which was far beyond the normal range. Chest computed tomography revealed hole sign in the right upper lobe and localized patchy clouding opacity with consolidation in the left lower lobe (Figure 1).
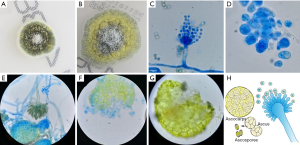
Grew floccose mold colonies after 9 days of incubation on Sabouraud dextrose agar could be observed from the sputum culture. These colonies displayed brownish green at the beginning, then presented yellow center. Microscopic appearance with lactophenol cotton blue staining showed predominant features consistent with Aspergillus glaucus. These included vesiculate conidiophores and ascocarps. Phialides covered the entire surface of the vesicle. The round yellow ascocarps showed on the third days by the slide culture method. Matured ascocarps released ascus, in which there were eight ascospores (Figure 2). Therefore, invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA) was probably diagnosed and voriconazole was initiated (intravenous medication, 200 mg q12 h).
Although Aspergillus glaucus is ubiquitous in warm moist environments, few cases of infections like IPA caused by the pathogen has been reported. Voriconazole might be one better choice to treat the diseases. However, the patient discharged voluntarily from the hospital without remission of symptoms after four days therapy and died one week later. Culture of Aspergillus glaucus from sputum sample is difficult since the organism requires at least about one week to grow on Sabouraud dextrose agar. Such a characteristic leads to the diagnosis of Aspergillus glaucus infection more complicated without a high index of clinical suspicion. An experienced microbiologist with better identification methods are more important in the process of disease diagnosis and treatment.
Acknowledgements
Funding: This work was supported by the Scientific Research Project of Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau (No. 201840006).
Footnote
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Informed Consent: Informed consent was obtained for the use of information and images. The patient’s identity has been kept confidential.
Cite this article as: Xu C, Li S, Zhou M, Yu Y. Pulmonary infection caused by Aspergillus glaucus in patient with leucocythemia. J Emerg Crit Care Med 2019;3:18.


